How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision inspections. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding your drone’s components and pre-flight checks to mastering basic and advanced flight maneuvers, and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone flight controls, camera operation, and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re well-equipped to confidently take to the skies.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to navigate the exciting realm of drone operation with confidence and competence. We’ll demystify the technology, simplify the procedures, and equip you with the knowledge to operate your drone responsibly and achieve stunning results.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s functionality, and familiarity with their functions will aid in troubleshooting and maintenance.
Drone Component Breakdown
| Component | Function | Importance | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust, enabling flight. | Essential for lift and maneuverability. Damage can lead to immediate loss of control. | Inspect for cracks or damage before each flight. Replace damaged propellers immediately. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers. | Provide the power for propulsion. Motor failure results in loss of control or inability to fly. | Check for unusual sounds or vibrations. Ensure proper motor mounting. |
| Flight Controller | Processes sensor data and controls motor speeds to maintain stability and execute commands. | The brain of the drone, responsible for stability and responsiveness. Malfunction can lead to erratic flight. | Calibrate the flight controller regularly. Check for loose connections. |
| Battery | Powers the drone’s electronics and motors. | Provides the energy for flight. Insufficient power leads to reduced flight time and potential crashes. | Ensure proper charging procedures. Monitor battery voltage and health. Replace aged batteries. |
| GPS | Provides location data for precise positioning and autonomous flight modes. | Crucial for accurate navigation and return-to-home functionality. GPS signal loss can impair flight. | Ensure clear view of the sky for optimal GPS signal reception. |
| Camera | Captures images and videos. | Provides aerial photography and videography capabilities. | Check lens for smudges or obstructions. Ensure proper camera settings. |
Drone Battery Types and Flight Time
Drone batteries are typically Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries. Different LiPo battery configurations (voltage and capacity) significantly affect flight time and performance. Higher capacity batteries generally offer longer flight times, but also increase the drone’s weight, potentially reducing maneuverability. For example, a 3S 1500mAh battery might provide 15-20 minutes of flight time, while a 4S 3000mAh battery could provide 25-35 minutes, but at a higher weight.
Drone Propeller Types and Performance
Propellers come in various sizes and designs, each impacting flight characteristics. Larger propellers generally provide more thrust and lift, while smaller propellers allow for greater maneuverability. Different blade designs (e.g., thin, thick, curved) also affect efficiency and noise levels. A propeller’s pitch (angle of the blade) influences speed and power. A higher pitch propeller provides more speed, while a lower pitch propeller provides more lift.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring a safe and successful flight. Overlooking even minor details can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist

- Check battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Inspect propellers for cracks, chips, or damage. Replace if necessary.
- Verify GPS signal strength. Ensure a clear view of the sky.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check all connections to ensure they are secure.
- Inspect the drone’s body for any damage.
- Review the planned flight path and ensure it is safe and legal.
Compass and IMU Calibration
Calibrating the compass and IMU is crucial for accurate flight and stability. These sensors provide data to the flight controller, enabling it to maintain orientation and position. Improper calibration can lead to erratic behavior and loss of control. Most drones have a built-in calibration procedure, typically involving rotating the drone slowly in various directions.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual flowchart, while not included here in HTML format, would ideally depict a sequence starting with battery check, moving to propeller inspection, then compass/IMU calibration, followed by GPS signal confirmation, and finally, a visual confirmation of the flight area’s safety and clearance. This flowchart should end with a “Ready for Takeoff” confirmation step.
Taking Off and Landing: How To Operate A Drone
Proper takeoff and landing techniques are crucial for safe drone operation. These procedures vary depending on the environment and wind conditions.
Takeoff Procedures (Open Field)
- Place the drone on a level surface.
- Ensure adequate space around the drone.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal lock.
- Slowly increase throttle to initiate takeoff.
- Maintain a steady ascent.
Takeoff Procedures (Confined Space)
- Choose a location with minimal obstacles.
- Perform a careful assessment of the surroundings.
- Execute a slow and controlled ascent.
- Maintain awareness of the drone’s position at all times.
Landing Procedures
- Slowly decrease throttle to initiate descent.
- Maintain a steady descent rate.
- Prepare for landing by selecting a suitable landing spot.
- Gently set the drone down on a level surface.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Wind Conditions
Wind significantly impacts takeoff and landing. In windy conditions, it’s crucial to select a sheltered location and perform a slow, controlled ascent and descent. Adjusting the drone’s orientation to compensate for wind gusts might be necessary.
Hazards and Mitigation
Potential hazards include obstacles, uneven terrain, and strong winds. Mitigation strategies involve careful pre-flight planning, choosing appropriate locations, and maintaining a safe distance from obstacles. Always be aware of your surroundings.
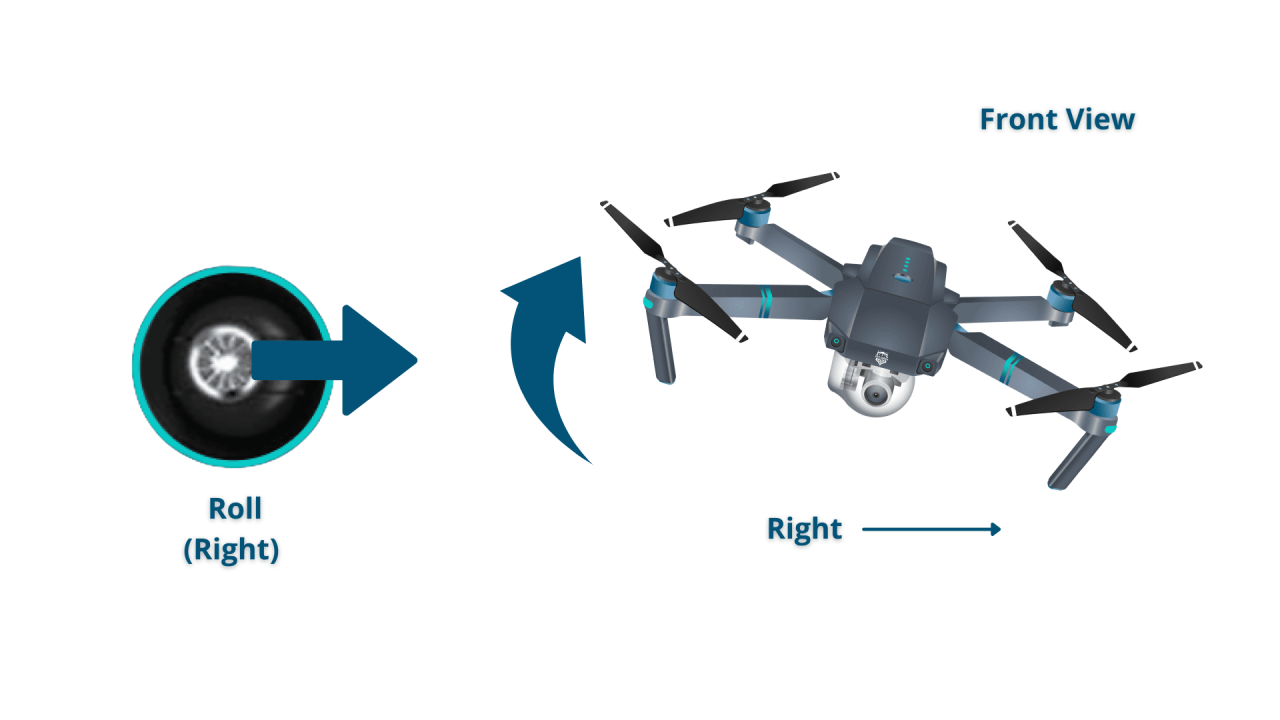
Basic Drone Flight Controls
Understanding the basic flight controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. These controls allow you to manipulate the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space.
Basic Flight Control
| Control | Function | Effect on Drone | Tips for Smooth Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throttle | Controls altitude. | Increases or decreases the drone’s height. | Use gentle, smooth movements to avoid abrupt changes in altitude. |
| Pitch | Controls forward and backward movement. | Moves the drone forward or backward. | Avoid jerky movements; use small, controlled adjustments. |
| Roll | Controls left and right movement. | Moves the drone left or right. | Maintain smooth and consistent movements to avoid sudden drifts. |
| Yaw | Controls rotation around the vertical axis. | Turns the drone left or right. | Use small increments for precise turning. |
Drone Flight Path Illustration
Imagine a drone starting at point A. Pushing the pitch control forward moves the drone to point B (forward). Pushing the roll control to the right moves the drone to point C (right). Increasing throttle moves the drone to point D (up). Using yaw control rotates the drone at point E (clockwise rotation).
The path would be illustrated with arrows: A → B → C → D → E, showing the combined effects of the controls.
Drone Stability
Maintaining drone stability requires smooth and controlled inputs to the flight controls. Avoid abrupt movements and sudden changes in direction. The drone’s flight controller helps maintain stability, but operator skill is crucial.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Once comfortable with basic controls, you can explore advanced maneuvers that expand your aerial capabilities.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Advanced maneuvers include orbiting a subject, following a pre-programmed waypoint path (often using waypoints set in drone software), and executing precise, complex flight paths for cinematic shots. These maneuvers typically rely on the drone’s GPS and advanced flight modes.
Flight Modes
GPS mode uses GPS data for precise positioning and stability. Attitude mode relies on the drone’s IMU and other sensors for orientation and control, offering greater maneuverability in GPS-denied environments, but requiring more pilot skill to maintain stability. Different drones offer varying flight modes and capabilities.
Flight Controller Influence
The flight controller significantly impacts maneuverability. Higher-end flight controllers offer advanced features like precise control, improved stability, and support for more complex flight modes. The choice of flight controller often determines the drone’s overall performance and capabilities.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial footage requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques.
Camera Setting Adjustments
Aperture, shutter speed, and ISO are key settings. Aperture controls depth of field (wide aperture for blurred backgrounds, narrow for sharp focus). Shutter speed affects motion blur (faster speeds freeze motion, slower speeds create motion blur). ISO controls sensitivity to light (higher ISO for low-light situations, but with potential for increased noise).
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Different angles provide unique perspectives. High-angle shots offer wide views, while low-angle shots emphasize scale and detail. Side angles and oblique shots add dynamic perspectives. Experimentation is key to finding the best angles for your subject.
Drone Photography/Videography Project Planning
- Define the project goals and desired shots.
- Scout the location and plan the flight path.
- Check weather conditions and ensure safe flying conditions.
- Adjust camera settings for optimal image quality.
- Execute the flight plan, capturing the desired shots.
- Review and edit the footage.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Drone operation carries inherent risks, and adherence to regulations is mandatory.
Safety Risks
Potential risks include collisions with obstacles, battery fires (due to improper handling or damaged batteries), loss of control due to technical malfunction or pilot error, and damage to property or injury to people.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Regulations vary by country and region. It is crucial to familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations governing drone operation in your area. These regulations often include restrictions on flight altitudes, proximity to airports, and required registrations.
Drone Safety Checklist
- Pre-flight inspection (battery, propellers, GPS).
- Check weather conditions and wind speed.
- Maintain visual line of sight.
- Avoid flying near people or obstacles.
- Adhere to airspace restrictions.
- Post-flight inspection (battery, propellers).
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues can save time and prevent further damage.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
- Low battery: Charge the battery fully. Consider a higher capacity battery for longer flight times.
- GPS signal loss: Ensure a clear view of the sky. Try restarting the drone and controller.
- Motor malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage. Check motor connections.
- Drone unresponsive: Try restarting the drone and controller. Check battery level.
- Camera malfunction: Check camera settings. Ensure lens is clean.
Interpreting Error Messages

Familiarize yourself with the error messages displayed on your drone’s remote controller. These messages often provide clues to diagnose problems. Consult your drone’s manual for explanations of specific error codes.
Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity. This includes cleaning the drone, inspecting propellers and motors, and checking battery health. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance is crucial.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. This guide has provided a foundational framework, covering the essential aspects of pre-flight preparation, basic and advanced flight controls, safe operating procedures, and essential troubleshooting techniques. By consistently practicing safe flight procedures and continuously refining your skills, you can unlock the full potential of your drone and capture incredible aerial perspectives.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and effective flights. Ultimately, responsible operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of your drone’s capabilities.
Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to all relevant regulations.
FAQ Overview
What is the best way to store my drone battery?
Store your drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Ideally, store them at around 50% charge to prolong their lifespan.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a significantly different location or if the drone’s orientation has been drastically altered.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (e.g., Attitude mode) and carefully bring it down to a safe landing. Avoid attempting complex maneuvers.
How do I clean my drone propellers?
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is a comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Gently clean your drone propellers with a soft cloth and mild detergent. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
