Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it? This respiratory virus, similar to RSV and influenza, is causing concern. This article breaks down what HMPV is, its symptoms, how it spreads, and what parents and caregivers can do to protect their children. We’ll explore the current situation in China, focusing on the challenges and the steps being taken to manage the outbreak.
Get ready to learn the facts and understand how to best protect your family.
So, HMPV is hitting Chinese kids hard right now – it’s a respiratory virus causing a lot of worry. It’s a reminder that illnesses spread quickly, and sometimes seemingly unrelated news highlights this; for example, check out this hockey injury report – Canucks: Dakota Joshua leaves game with apparent leg injury – which shows how easily things can go wrong.
Getting back to HMPV, understanding its spread is key to protecting vulnerable populations.
We’ll cover everything from the virus’s characteristics and transmission to preventative measures and treatment options. We will also delve into the specific impact of this surge in China, exploring the contributing factors and the response of the healthcare system. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of HMPV and how to navigate this concerning health issue.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Surge in China: Understanding the Virus and its Impact
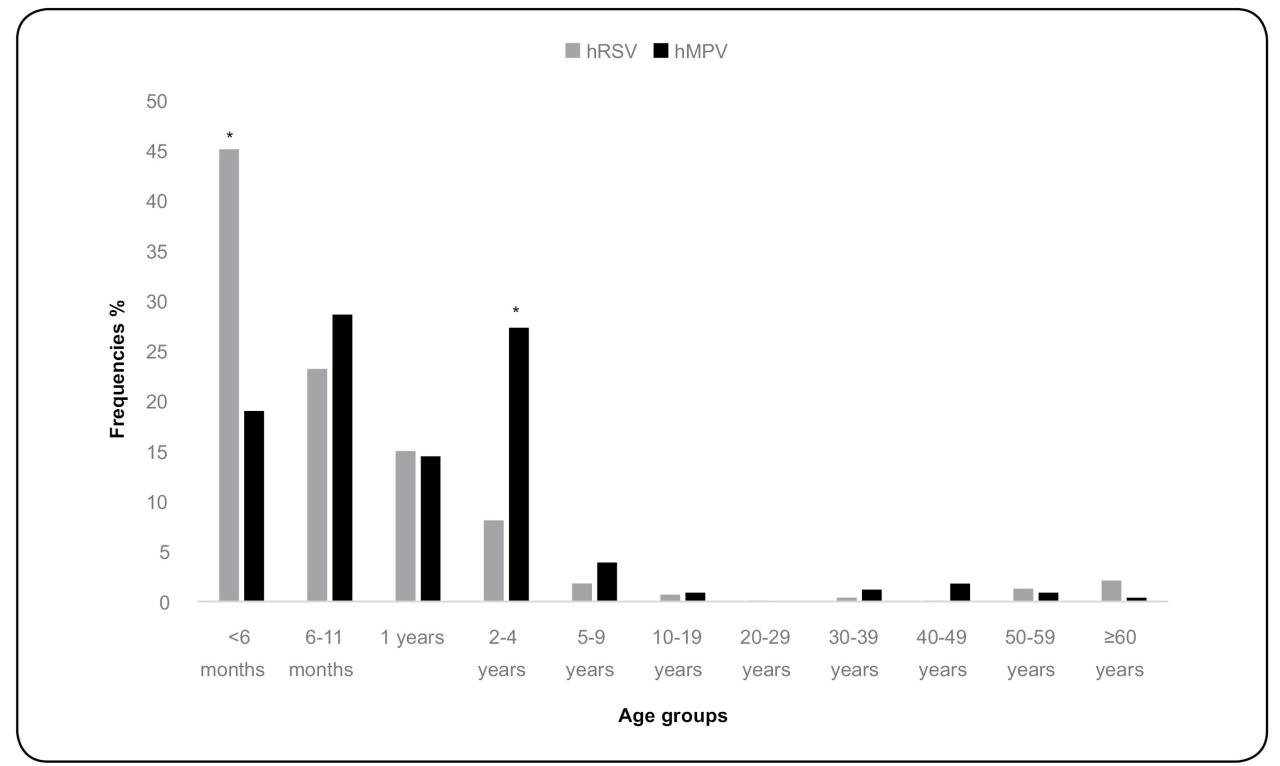
A recent surge in Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) cases among children in China has raised concerns. This article provides information on HMPV, its impact on children in China, and strategies for prevention and treatment.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV): Characteristics, Symptoms, and Differentiation from Other Viruses
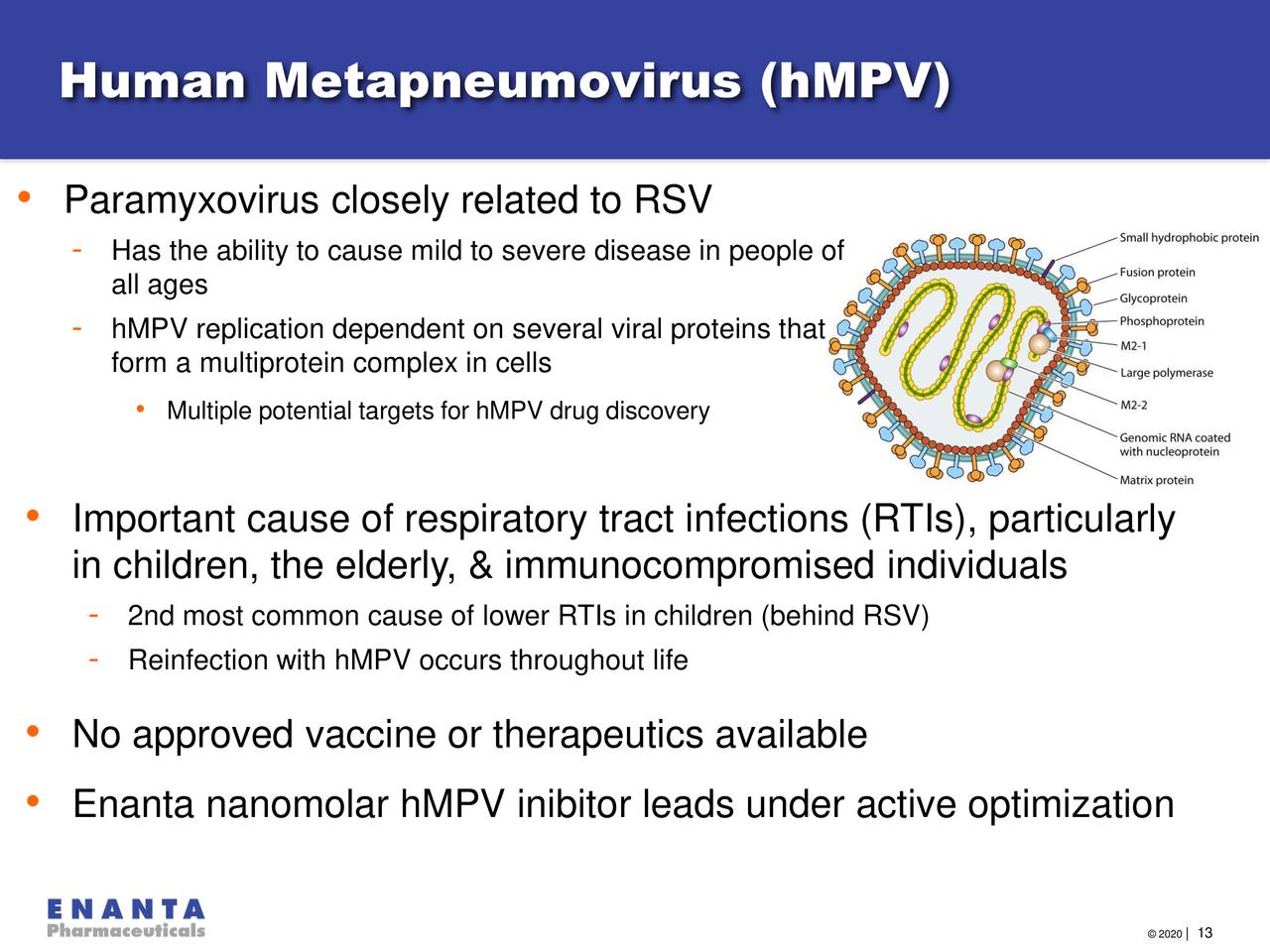
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common respiratory virus belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family. It’s characterized by a single-stranded RNA genome and a lipid envelope studded with surface glycoproteins. Transmission occurs primarily through respiratory droplets produced during coughing or sneezing. In children, HMPV infection often manifests as mild upper respiratory symptoms like runny nose, cough, and fever.
However, more severe lower respiratory tract infections, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, can also occur, especially in infants and young children with underlying health conditions. HMPV differs from other respiratory viruses like RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) and influenza in several key aspects, including its genetic makeup and the severity of infections it causes.
HMPV Symptom Comparison with RSV and Influenza, Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it?
The following table highlights the key differences between HMPV, RSV, and influenza in terms of symptoms, transmission, and severity in children.
| Virus Name | Symptoms | Transmission | Severity in Children |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMPV | Runny nose, cough, fever, wheezing, bronchiolitis (in severe cases) | Respiratory droplets | Can range from mild to severe, particularly in infants and those with pre-existing conditions. |
| RSV | Runny nose, cough, fever, wheezing, bronchiolitis, pneumonia | Respiratory droplets, contact | Can be severe, especially in infants and young children. |
| Influenza | Fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, fatigue | Respiratory droplets, contact | Severity varies; can cause severe illness, especially in young children, the elderly, and those with underlying health conditions. |
HMPV’s Impact on Children in China: Case Surge and Contributing Factors
While precise data on the current HMPV surge in China is constantly evolving and may not be publicly available in a comprehensive, readily accessible form, reports indicate a significant increase in cases, particularly among young children. This increase may be attributed to several factors. Seasonal variations play a role, with HMPV infections often peaking during certain times of the year.
High population density in urban areas could facilitate the rapid spread of the virus. Limited access to healthcare in some regions might also contribute to underreporting and delayed treatment, potentially leading to more severe outcomes. The severity of HMPV infections in Chinese children varies, with some requiring hospitalization due to pneumonia or bronchiolitis. Mortality data is likely underreported and requires further investigation.
- Challenges in the Chinese healthcare system include potential strain on hospital resources due to increased patient numbers.
- Difficulties in rapid diagnosis and effective case management.
- Uneven distribution of healthcare resources across different regions.
- Potential shortages of medical personnel and supplies.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies for HMPV Infections
Preventing HMPV infection relies heavily on measures that limit the spread of respiratory viruses. Good hand hygiene, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water, is crucial. While a specific HMPV vaccine is not yet widely available, vaccines against other respiratory viruses like influenza can provide some indirect protection by reducing the overall burden on the respiratory system.
Social distancing, particularly during peak infection seasons, can also help reduce transmission.
Treatment for HMPV infections primarily focuses on supportive care, managing symptoms such as fever and cough with over-the-counter medications. For severe cases, particularly in infants and children with underlying conditions, antiviral medications might be considered. However, the use of antivirals for HMPV is still under investigation, and their effectiveness is not definitively established.
HMPV Case Management Flowchart
A flowchart for managing HMPV cases would start with an initial assessment of the child’s symptoms. Based on the severity of symptoms, decisions would be made regarding supportive care at home versus hospitalization. Hospitalized children would receive more intensive monitoring and treatment, including oxygen therapy if needed. Discharge criteria would include improvement in respiratory symptoms and vital signs.
So, HMPV is causing a surge in sick kids in China – it’s a respiratory virus, kinda like RSV. It’s a bummer to hear about that, reminds me of how worrying injuries are in sports, like what happened to Dakota Joshua – check out this article if you want details: Canucks: Dakota Joshua leaves game with apparent leg injury.
Anyway, back to HMPV, keeping an eye on its spread is important, especially with vulnerable young ones.
Public Health Response and Recommendations
Public health recommendations for parents and caregivers should emphasize preventative measures such as hand hygiene, cough etiquette, and seeking medical attention if symptoms worsen. Public health agencies play a vital role in monitoring HMPV activity, providing timely information to healthcare providers, and implementing strategies to mitigate outbreaks.
- Public Awareness Campaign: A hypothetical campaign could utilize television and radio public service announcements, social media campaigns, and educational materials distributed through schools and healthcare facilities. Key messages would focus on the importance of hand hygiene, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely medical care.
- Infographic Illustration: A simple infographic could depict a child with a runny nose and cough, illustrating common HMPV symptoms. A section could highlight the importance of handwashing with soap and water. Another section could show a doctor examining a child, emphasizing the need for timely medical attention. A final section could depict a family practicing social distancing during peak season, highlighting the role of preventative measures.
Summary
The rise of HMPV in China highlights the importance of vigilance and proactive measures to protect children. Understanding the virus, its transmission, and preventative strategies empowers parents and healthcare systems to effectively manage outbreaks. While there’s no specific vaccine yet, simple steps like hand hygiene and staying home when sick can make a significant difference. Remember, staying informed and taking preventative actions are key to keeping children healthy during this surge.
Expert Answers: Viral Disease HMPV Is On The Rise Among Kids In China — What Is It?
Is HMPV contagious?
Yes, HMPV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
So, HMPV is hitting Chinese kids hard right now – it’s a nasty respiratory virus. Thinking about the scale of this outbreak, it makes you realize just how much medical manufacturing happens in China; check out this article about its manufacturing power: China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. That means a lot of the medical supplies needed to combat this HMPV surge likely originate there, highlighting the interconnectedness of global health and manufacturing.
How long does HMPV last?
Most HMPV infections resolve within 1-2 weeks, but some can be more severe and prolonged.
What’s the difference between HMPV and the flu?
While both cause respiratory illness, HMPV is distinct genetically and may cause slightly different symptoms. Flu often involves more pronounced body aches and fever.
Are there any long-term effects of HMPV?
While most children recover fully, severe HMPV infections can rarely lead to long-term respiratory issues in some cases.